Third-party certification systems play a pivotal role in ensuring accountability, transparency, and trust across industries and markets. They help organizations meet rigorous standards, and enhance stakeholder trust by providing reliable, verified data and information. As ISEAL (the global membership organization for credible sustainability standards) highlights, “Sustainability standards continue to be one of the most important tools to support businesses across the value chain deliver on core sustainability issues.” In this series of articles, we explore the four key characteristics and associated benefits of third-party certification systems. With a particular focus on EDGE Certification, the global standard for workplace diversity, equity, and inclusion, we demonstrate how certification gender equity, and gender and intersectional equity is a powerful tool that can drive inclusive economic growth and create respectful work environments for all.
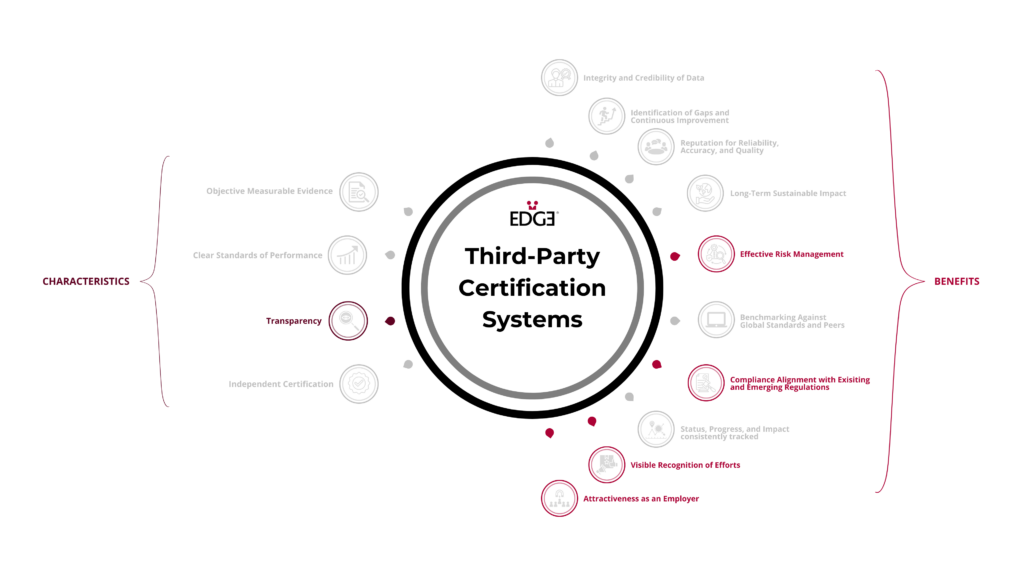
Third-party certification systems are based on an independent audit of an organization’s relevant data and information, and provide transparency to key organizational stakeholders on the level of performance attained, as well as comfort that the organization’s policies and practices are credible and verified. Furthermore, such systems can promote transparency by encouraging or requiring organizations to disclose their related data and information.
EDGE Certification provides a structured framework and foundation for organizations to be able to both manage and communicate on their relevant DE&I performance data, information, and efforts. EDGE Certification offers certified organizations a credible and externally verified way, through the EDGE Certification Seal, to communicate their commitment to gender and intersectional equity, providing a visible recognition of their efforts. It can also support organizations to meet regulatory disclosure requirements. There are a number of emerging regulations covering the disclosure of DE&I data and information, such as the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, the EU Pay Transparency Directive, and a multitude of national level regulations.
There is an increasing body of research indicating that consumers, employees, and prospective employees place a high value on transparency when deciding whether to engage with a particular organization. Transparency, on where an organization stands on a particular topic such as DE&I in the workplace, is essential for building trust and confidence with stakeholders such as these. Greater transparency has been linked to an increase in an organization’s credibility, it’s attractiveness as an investment, as a business partner, and as an employer, thereby gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace. Conversely, a lack of transparency can be seen to impede informed decision-making, making it difficult for investors to evaluate a company’s performance and for potential employees to find companies that align with their values. Transparency also acts as a risk reduction strategy, helping organizations to build brand reputation, and maintain trusted relationships with their stakeholders.
We hope you are finding our series on third-party certification systems insightful. In the next article, we’ll wrap up with a closer look at the power of independent certification—an essential mechanism for ensuring long-term, measurable impact, driving continuous improvement, and building accountability.





